How Thick is Too Thick When Installing Polyiso Roof Insulation?
The answer may seem obvious, but understanding the reasons why are important to a roof's integrity

Photo credit: PIMA
Polyisocyanurate, or polyiso, roof insulation boards provide a versatile and energy-efficient solution for low-slope commercial roofing projects. From new construction to reroof projects on existing buildings, polyiso’s high R-value allows project teams to meet energy code targets with less material than alternative products.
Polyiso roof insulation boards are manufactured with different facer types that deliver strength, dimensional stability, and unique properties for various applications. Polyiso high-density roof cover boards and tapered insulation products complete the portfolio of polyiso roofing products that deliver performance for any roofing project.
What Are the Available Thicknesses of Polyiso Insulation Boards?
Manufacturers produce polyiso roof insulation boards in a wide range of thicknesses. This allows project teams to specify products based on individual project needs and code requirements. Typical thicknesses for polyiso insulation range from 1 inch (25.4 mm) to 4.5 inches (114.3 mm).
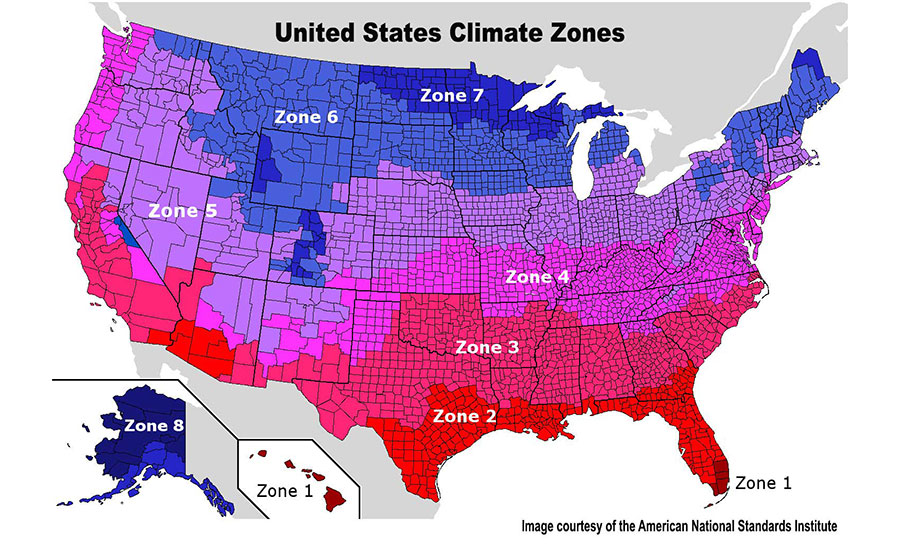
Regarding popularity, 2.6-inch (66 mm) thick polyiso roof insulation boards are often specified. Two layers of 2.6-inch thick polyiso insulation deliver a total of R-30, equating to the code-required minimum for above-deck roof insulation for commercial buildings in ASHRAE Climate Zones 4-6 in the United States.
These climate zones represent a significant portion of annual construction activity. Thicker products — such as 4-inch thick polyiso boards — may commonly be used as infill panels for tapered insulation systems.

Multi-layered installation of roof insulation boards can bolster thermal efficiency and mitigate moisture migration.
Image courtesy of PIMA.
How Thick is Too Thick?
Project teams may ask whether installing thicker polyiso roof insulation boards should be avoided. The answer is no. Manufacturers provide installation requirements for polyiso roof insulation, which may include specific instructions based on the thickness of the insulation boards used.
The National Roofing Contractors Association (NRCA) had previously recommended a maximum board thickness of 2.5 inches for polyiso roof insulation boards. However, the nominal recommendation has been deleted in the most recent version (2023) of “The NRCA Roofing Manual: Membrane Roof Systems.” The NRCA manual now directs users to consult the manufacturer-published installation instructions for recommended application procedures. See Section 4.9—Polyisocyanurate of the NRCA manual for additional details.
Why Are Multi-Layered Roof Insulation Systems Important?
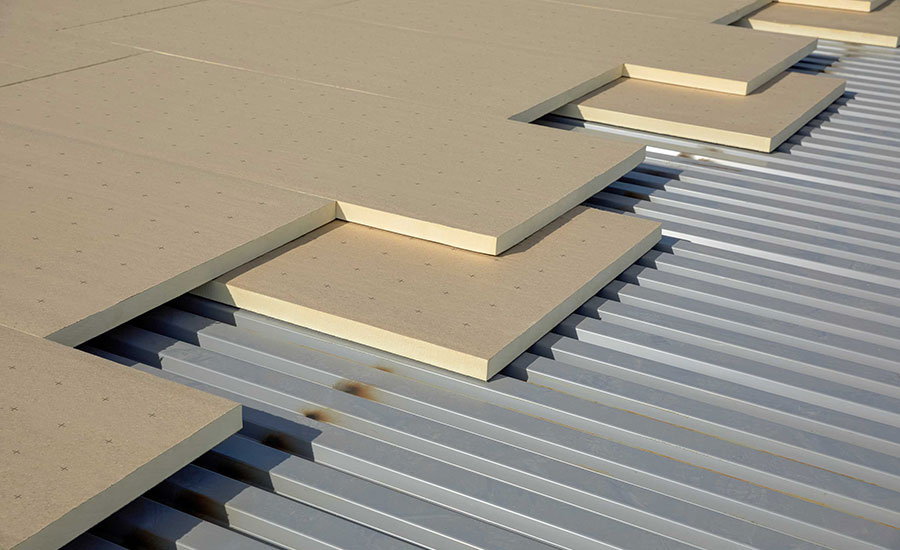
Rigid insulation boards such as polyiso insulation should be installed in multiple layers, with the joints of each layer staggered. The multi-layered installation of roof insulation boards is an industry best practice rooted in building science fundamentals and is required by modern energy codes.
The benefits include:
Reduced thermal losses at insulation joints
Reduced thermal bridging from fasteners (when adhering to the top insulation layer)
Reduced air leakage
Reduced moisture migration in the roof system to the underside of the roof membrane (which can lead to possible condensation)
Reduced potential for membrane buckling, ridging, and splitting
The NRCA manual also suggests that multi-layered roof insulation systems can increase the dimensional stability of the overall insulation system. Additionally, project teams should include a roof cover board as part of any system. Roof cover boards provide a suitable substrate for membrane attachment and enhance the durability of the roof system. This is especially important for roofs subject to extreme weather events (e.g., hail, high winds), consistent service traffic, or roof areas with renewable energy systems such as rooftop solar. Polyiso high-density roof cover boards are lightweight, easy-to-handle options that also deliver added insulation performance (R-2.5 for 0.5-inch [12.7 mm] thick products).
Additional Information
Project teams should always consult the manufacturer-published installation instructions for polyiso products. The Polyisocyanurate Insulation Manufacturers Association (PIMA) maintains a library of technical bulletins to support using polyiso roof insulation.
The following technical bulletins provide additional information on the topics discussed in this article: “PIMA Technical Bulletin No. 113 — Benefits of Multiple Polyiso Roof Insulation Layers with Staggered Joints” and “PIMA Technical Bulletin No. 118 — Recommended Polyiso Insulation Thicknesses for Meeting Commercial Roof Prescriptive R-value Requirements.”
For these resources and more information on polyiso insulation, visit polyiso.org.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!